Bernard Krauth Wilson 2009
From Werner KRAUTH
| Revision as of 10:22, 10 November 2011 Werner (Talk | contribs) (→Python Implementation) ← Previous diff |
Revision as of 10:34, 10 November 2011 Werner (Talk | contribs) (→Illustration:) Next diff → |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
| [http://arxiv.org/pdf/0903.2954v2 Electronic version (from arXiv)] | [http://arxiv.org/pdf/0903.2954v2 Electronic version (from arXiv)] | ||
| - | =Illustration:= | + | =Illustration= |
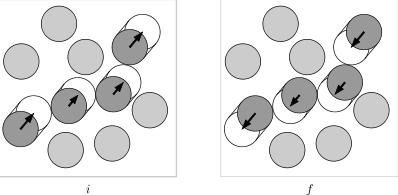
| - | [[Image:Event chain move2.jpg|left|150px|border|Move of the Event-chain algorithm]] | + | [[Image:Event chain move2.jpg|left|150px|border|Move of the Event-chain algorithm]] Here is the basic schema of the event-chain algorithm (the added length of the arrows equals a fixed value <math>l</math>. The event-chain algorithm is microreversibility and it has no rejections. In our applications, we use a version of the algorithm where particles move |
| + | either in the <math>+x</math> or the <math>+y</math> direction. This is also done in the below Python implementation. | ||
| <br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
Revision as of 10:34, 10 November 2011
E. P. Bernard, W. Krauth, D. B. Wilson Event-chain algorithms for hard-sphere systems Physical Review E 80 056704 (2009)
Contents |
Paper
Abstract: In this paper we present the event-chain algorithms, which are fast Markov-chain Monte Carlo methods for hard spheres and related systems. In a single move of these rejection-free methods, an arbitrarily long chain of particles is displaced, and long-range coherent motion can be induced. Numerical simulations show that event-chain algorithms clearly outperform the conventional Metropolis method. Irreversible versions of the algorithms, which violate detailed balance, improve the speed of the method even further. We also compare our method with a recent implementations of the molecular dynamics algorithm.
Further information: We used this algorithm, which is about 100 times faster than the local Metropolis algorith, for our work on the liquid-hexatic transition in two-dimensional hard disks.
Electronic version (from arXiv)
Illustration
Here is the basic schema of the event-chain algorithm (the added length of the arrows equals a fixed value <math>l</math>. The event-chain algorithm is microreversibility and it has no rejections. In our applications, we use a version of the algorithm where particles moveeither in the <math>+x</math> or the <math>+y</math> direction. This is also done in the below Python implementation.
Python Implementation
Here is a basic python implementation of the straight event-chain algorithm for four disksin the version breaking detailed balance. A randomly disk always moves in the +x direction. At each step, the configuration is translated (and flipped) so that the moves starts at <math>(x,y)=(0.,0.)</math>.
###========+=========+=========+=========+=========+=========+=========+=
## PROGRAM : event_chain.py
## TYPE : Python script (python 2.7)
## PURPOSE : Event-chain simulation for 4 particles in a square box
## with periodic boundary conditions.
## COMMENT : L is a list of tuples, move is always in +x direction
## Flip_conf exchanges x and y (effective move in +y direction)
## VERSION : 10 NOV 2011
##========+=========+=========+=========+=========+=========+=========+
from random import uniform, randint, choice, seed
import math, pylab, sys, cPickle
def dist(x,y):
"""periodic distance between two two-dimensional points x and y"""
d_x= abs(x[0]-y[0])%box
d_x = min(d_x,box-d_x)
d_y= abs(x[1]-y[1])%box
d_y = min(d_y,box-d_y)
return math.sqrt(d_x**2 + d_y**2)
def Flip_conf(L,rot):
L_flip = []
for (a,b) in L:
if rot == 1: L_flip.append((box - b,a))
else: L_flip.append((b,box - a))
return L_flip,-rot
#=========================== main program starts here =========================================
box = 4.0
data = []
L = [(1.,1.),(2.,2.),(3.,3.),(3.,1.)] # initial condition
rot = 1
ltilde = 0.9
for iter in xrange(1000000):
if iter%10000 == 0: print iter
i = randint(0,3)
j = (i + randint(1,3))%4
data.append(dist(L[i],L[j]))
if randint(0,1) < 1: L,rot = Flip_conf(L,rot)
Zero_distance_to_go = ltilde
next_particle = choice(L)
while Zero_distance_to_go > 0.0:
#
# this iteration will stop when the Zero_distance_to_go falls to zero
#
L.remove(next_particle)
L = [((x[0]-next_particle[0])%box,(x[1]-next_particle[1])%box) for x in L]
next_position,next_particle = (float("inf"),(float("inf"),0.0))
Current_position = 0.0
for x in L:
x_image = list(x)
if x[0]> box/2: x_image[0] = x[0] - box
if x[1]> box/2: x_image[1] = x[1] - box
if abs(x_image[1]) < 1.0:
x_dummy = x_image[0] - math.sqrt(1.0 - x_image[1]**2)
if x_dummy > 0.0 and x_dummy < min(Zero_distance_to_go,next_position):
next_position,next_particle = (x_dummy,x)
distance_to_next_event = next_position - Current_position
if Zero_distance_to_go < distance_to_next_event:
Current_position += Zero_distance_to_go
L.append((Current_position,0.0))
break
else:
Current_position += distance_to_next_event
Zero_distance_to_go -= distance_to_next_event
L.append((Current_position,0.0))
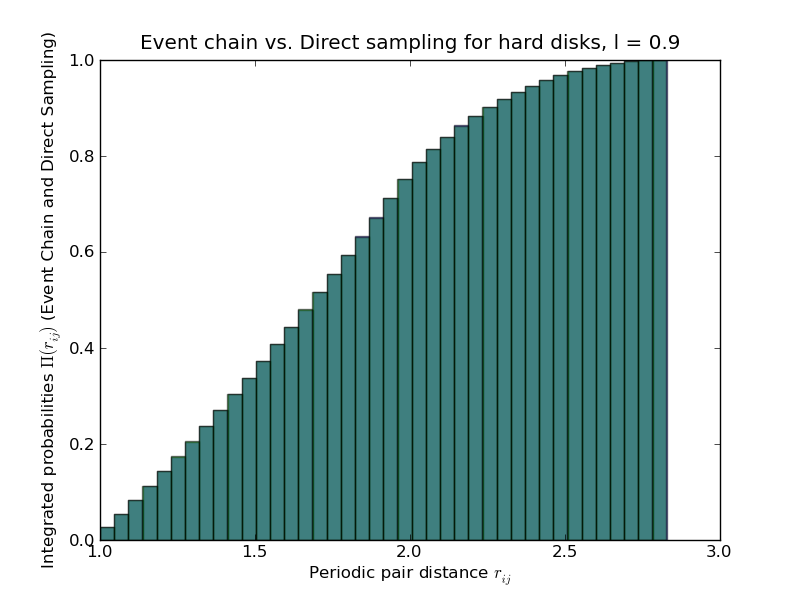
pylab.hist(data,bins=40,normed=True,alpha=0.5,cumulative=True)
pylab.title("Event chain for four hard disks, l = "+str(ltilde))
pylab.xlabel("Periodic pair distance $r_{ij}$")
pylab.ylabel("Integrated probabilities $\Pi(r_{ij})$")
pylab.savefig('Event_chain'+str(ltilde)+'.png')
pylab.show()
Comparison of output with direct-sampling algorithm