Kapfer Krauth 2016
From Werner KRAUTH
S. C. Kapfer, W. Krauth Cell-veto Monte Carlo algorithm for long-range systems arXiv:1606.06780 (2016)
Paper
Abstract We present a rigorous efficient event-chain Monte Carlo algorithm for long-range interacting particle systems. Using a cell-veto scheme within the factorized Metropolis algorithm, we compute each single-particle move with a fixed number of operations. For slowly decaying potentials such as Coulomb interactions, screening line charges allow us to take into account periodic boundary conditions. We discuss the performance of the cell-veto Monte Carlo algorithm for general inverse-power-law potentials, and illustrate how it provides a new outlook on one of the prominent bottlenecks in large-scale atomistic Monte Carlo simulations.
Electronic version (from arXiv)
Illustration
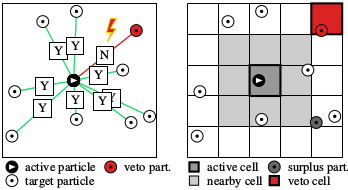
The cell-veto algorithm is an application of the event-chain paradigm that was developed in 2009, with E. P. Bernard and D. B. Wilson, and much extended together with M. Michel and S. C. Kapfer, where we introduced the factorized Metropolis algorithm. In this algorithm, unlike in 99.9% of all simulation algorithms (Monte Carlo or Molecular dynamics), one does not compute the system energy in order to decide on a change of the physical system, but rather looks at all the interactions separately. So, if a particle a (the active particle) wants to move, it has to ask all its partners t_1, t_2, .... (the target particles). If there is only a single veto, the move is rejected. In the cell-veto algorithm (see the right side of the figure), the identification of the rejecting particle is preceeded by that of a veto cell. The advantage of this is that cell vetos can be identified immediately (in a constant number of operations, that is, in O(1)), and then instantly confirmed or infirmed on the particle level.Python implementation
The paper contains a Python demo implementation of the cell-veto algorithm
import math, random, sys, pylab
from copy import deepcopy
def CellRate(TargetCellLL, ActiveCellLL, L, CellBoundary): # always >= 0
Rate = 0.0
for a in CellBoundary:
for b in CellBoundary:
del_x = TargetCellLL[0] - ActiveCellLL[0] + (a[0] - b[0]) / L
del_y = TargetCellLL[1] - ActiveCellLL[1] + (a[1] - b[1]) / L
Rate = max(Rate, PairRate(del_x, del_y, k_max))
return Rate
def PairRate(del_x, del_y, k_max): # Here for 1/r potential in 2d
q = 0.0
for ky in range(-k_max, k_max + 1):
for kx in range(-k_max, k_max + 1):
q += (del_x + kx ) / (
(del_x + kx) ** 2 + (del_y + ky) ** 2) ** (3.0 / 2.0)
q += 1.0 / ((del_x + kx + 0.5) ** 2 + (del_y + ky) ** 2) ** (1.0 / 2.0)
q -= 1.0 / ((del_x - kx - 0.5) ** 2 + (del_y + ky) ** 2) ** (1.0 / 2.0)
return max(0.0, q)
def CellTranslate(TargetCell, ActiveCell): # TargetCell -> 0 as CellTranslate -> ActiveCell
kt_y = (TargetCell // L) % L
kt_x = (TargetCell - L * kt_y) % L
ka_y = (ActiveCell // L) % L
ka_x = (ActiveCell - L * ka_y) % L
delx = (kt_x + ka_x) % L
dely = (kt_y + ka_y) % L
return delx + dely * L
def CellIt(a): # Cell index for x,y positions
return int((a[0] % L) * L) + L * int((a[1] % L) * L)
def CellLimit(CellNumber): # Returns Rightmost x position. Can be used for x and y
return (CellNumber % L + 1) / float(L)
def dist(x,y):
"""periodic distance between two two-dimensional points x and y"""
d_x= abs(x[0] - y[0]) % 1.0
d_x = min(d_x, 1.0 - d_x)
d_y= abs(x[1] - y[1]) % 1.0
d_y = min(d_y, 1.0 - d_y)
return math.sqrt(d_x**2 + d_y**2)
def WalkerSet(pi_in):
pi = deepcopy(pi_in)
N_walker = len(pi)
walker_mean = sum(a[0] for a in pi) / float(N_walker)
long_s = []
short_s = []
for p in pi:
if p[0] > walker_mean:
long_s.append(p)
else:
short_s.append(p)
walker_table = []
for k in range(N_walker - 1):
e_plus = long_s.pop()
e_minus = short_s.pop()
walker_table.append((e_minus[0], e_minus[1], e_plus[1]))
e_plus[0] = e_plus[0] - (walker_mean - e_minus[0])
if e_plus[0] < walker_mean:
short_s.append(e_plus)
else:
long_s.append(e_plus)
if long_s != []:
walker_table.append((long_s[0][0], long_s[0][1], long_s[0][1]))
else:
walker_table.append((short_s[0][0], short_s[0][1], short_s[0][1]))
return N_walker, walker_mean, walker_table
def WalkerSample(walker_table, walker_mean, N_walker):
Upsilon = random.uniform(0.0, walker_mean)
i = random.randint(0, N_walker - 1)
if Upsilon < walker_table[i][0]:
return walker_table[i][1]
else: return walker_table[i][2]
CellBoundary = []
NStep = 10 # going around the boundary of a cell (naive)
for i in range(NStep):
x = i / float(NStep)
CellBoundary += [(x, 0.0), (1.0, x), (1.0 - x, 1.0), (0.0, 1.0 - x)]
histo = []
L = 10
NCell = L ** 2
NPart = 40
beta = 1.0
k_max = 2 # extension of periodic images.
CellLL = [(x / float(L), y / float(L)) for y in range(L) for x in range(L)]
CellExclude = [0, 1, L - 1, L, L + 1, 2 * L - 1, NCell - L, NCell - L + 1, NCell - 1]
QCell = []
for k in range(NCell):
if k in CellExclude: QCell.append([0, k])
else: Dummy = QCell.append([CellRate(CellLL[k], (0.0, 0.0), L,
CellBoundary), k])
QPrime = sum(a[0] for a in QCell) # cell rate
N_walker, walker_mean, walker_table = WalkerSet(QCell)
Particles = []
for k in range(NPart):
a = (random.uniform(0.0, 1.0), random.uniform(0.0, 1.0))
Particles.append(a)
for iter in range(10000):
if random.randint(0,1) == 1:
for k in range(NPart):
Particles[k] = (Particles[k][1], Particles[k][0])
Surplus = []
CellOcc = {}
ltilde = 0.18
for k in range(NPart):
a = Particles[k]
n_cell = CellIt(a)
if not CellOcc.has_key(n_cell):
CellOcc[n_cell] = a
else:
Surplus.append(a)
if random.uniform(0.0, 1.0) < len(Surplus) / float(NPart):
ActiveParticle = random.choice(Surplus)
Surplus.remove(ActiveParticle) # Active particle into Cell, not into Surplus
ActiveCell = CellIt(ActiveParticle)
if CellOcc.has_key(ActiveCell):
Surplus.append(CellOcc.pop(ActiveCell))
CellOcc[ActiveCell] = ActiveParticle[:]
else:
while True:
ActiveCell = random.randint(0, NCell - 1)
if CellOcc.has_key(ActiveCell):
ActiveParticle = CellOcc[ActiveCell]
break
ActiveCellLimit = CellLimit(ActiveCell)
distance_to_go = ltilde
while distance_to_go > 0.0:
PossibleActiveParticle= ActiveParticle[:]
Possible_distance_to_go = distance_to_go
ActiveCellChange = False
Lifting = False
while True:
DistanceLimit = PossibleActiveParticle[0] + Possible_distance_to_go
DelS =-math.log(random.uniform(0.0, 1.0)) / QPrime
if DistanceLimit < ActiveCellLimit and PossibleActiveParticle[0] + DelS > DistanceLimit:
PossibleActiveParticle = (DistanceLimit, PossibleActiveParticle[1])
Possible_distance_to_go = 0.0
break # Distance-to-go break
elif PossibleActiveParticle[0] + DelS > ActiveCellLimit:
Possible_distance_to_go -= (ActiveCellLimit - PossibleActiveParticle[0])
PossibleActiveParticle = (ActiveCellLimit % 1.0, PossibleActiveParticle[1])
ActiveCellChange = True
break #AC break
else:
PossibleActiveParticle = (PossibleActiveParticle[0] + DelS, PossibleActiveParticle[1])
Possible_distance_to_go -= DelS
TargetCell = WalkerSample(walker_table, walker_mean, N_walker)
cell_rate_active_target = QCell[TargetCell][0]
TargetCell = CellTranslate(TargetCell, ActiveCell)
if CellOcc.has_key(TargetCell):
TargetParticle = CellOcc[TargetCell]
Ratio = PairRate(TargetParticle[0] - PossibleActiveParticle[0], TargetParticle[1] -
PossibleActiveParticle[1], k_max) / cell_rate_active_target
delx = (TargetParticle[0] - PossibleActiveParticle[0]) % 1.0
dely = (TargetParticle[1] - PossibleActiveParticle[1]) % 1.0
if random.uniform(0.0, 1.0) < Ratio:
Lifting = True
break # Lifting break
#
# here the sr (naive and a bit approximate, as we suppose a constant rate)
#
ToBeChecked = Surplus[:]
for ECell in CellExclude:
DummyCell = CellTranslate(ECell, ActiveCell)
if CellOcc.has_key(DummyCell):
ToBeChecked.append(CellOcc[DummyCell])
ToBeChecked.remove(ActiveParticle)
DelSMax = PossibleActiveParticle[0] - ActiveParticle[0]
for PossibleTargetParticle in ToBeChecked:
QRateLoc = PairRate(PossibleTargetParticle[0] - ActiveParticle[0],
PossibleTargetParticle[1] - ActiveParticle[1], k_max)
if QRateLoc > 0.0:
DelS =-math.log(random.uniform(0.0, 1.0)) / QRateLoc
if DelS < DelSMax: # Displacement cannot
# interfere with cell boundaries or distance_to_go
Lifting = True
ActiveCellChange = False
Possible_distance_to_go = distance_to_go - DelS
DelSMax = DelS
TargetParticle = PossibleTargetParticle[:] # have to take into
# account that the TargetParticle may be a Surplus one...
PossibleActiveParticle = (ActiveParticle[0] + DelS,
PossibleActiveParticle[1])
ActiveParticle = PossibleActiveParticle[:] #First move, then lift
distance_to_go = Possible_distance_to_go
if ActiveCellChange:
NewActiveCell = CellIt((ActiveParticle[0] + 0.001, ActiveParticle[1])) # Naive
if CellOcc.has_key(NewActiveCell):
Surplus.append(CellOcc.pop(NewActiveCell))
CellOcc[NewActiveCell] = ActiveParticle[:]
CellOcc.pop(ActiveCell) # Active cell occupied by active particle
for a in Surplus:
if CellIt(a) == ActiveCell:
CellOcc[ActiveCell] = a
Surplus.remove(a)
break
ActiveCell = NewActiveCell
ActiveCellLimit = CellLimit(ActiveCell)
else:
CellOcc[ActiveCell] = ActiveParticle[:]
if Lifting:
if TargetParticle in Surplus:
TargetCell = CellIt(TargetParticle)
Surplus.remove(TargetParticle)
if CellOcc.has_key(TargetCell):
Surplus.append(CellOcc.pop(TargetCell))
CellOcc[TargetCell] = TargetParticle[:]
ActiveParticle = TargetParticle[:]
ActiveCell = CellIt(ActiveParticle) # Naive , zu verbessern
ActiveCellLimit = CellLimit(ActiveCell)
# Naive, Particles vector for x <-> y transfer
Particles = []
for k in range(NCell):
if CellOcc.has_key(k):
Particles.append(CellOcc[k])
Particles += Surplus
for k in range(NPart):
for l in range(k):
histo.append(dist(Particles[k], Particles[l]))
pylab.hist(histo, bins=100, range=(0.0, 1.0), normed=True)
pylab.title('Demo_cell, ECMC, $k_{\max}$ = ' + str(k_max) + ' $NPart$ = ' +
str(NPart))
pylab.savefig('eventchain.png')
pylab.show()